An EV works differently from a car that has a transmission. In cars with a transmission, gears turn at different speeds as the car shifts between forward and reverse gear. An EV does not have any type of transmission. Instead, an electric motor provides power directly to the wheels (as opposed to an internal combustion engine, or ICE). The motor turns at the same speed as the wheels it affects, resulting in forward and reverse motion without the need for a gearbox or other intermediary mechanisms. Read on to learn more about how EVs work without a clutch or a transmission.
What is an EV without a clutch?

The most basic way to power an EV is through the battery. This is what powers the motor and allows the car to move. The battery can hold the charge needed to power the car and can also be used to slow the car down. When the car is being driven, the battery is supplying the power. There is no transmission involved at all. EVs without a clutch use the same type of technology found in motorcycles. With no clutch pedal involved, these EVs allow the driver to simply turn the key and the car begins to move. These types of EVs are also called “proprietary” or “manual” EV.
How does an EV work without a transmission?
A transmission allows a car with an engine to change gears and move between forward and reverse. With an EV, the wheel that is powered by the battery is in direct contact with the road, and the rest of the vehicle’s wheels are powered by that wheel. The wheel that is being driven by the battery maintains a constant speed. There is no transmission in an EV, but there are different types of motors.
Batteries power an EV through regenerative braking
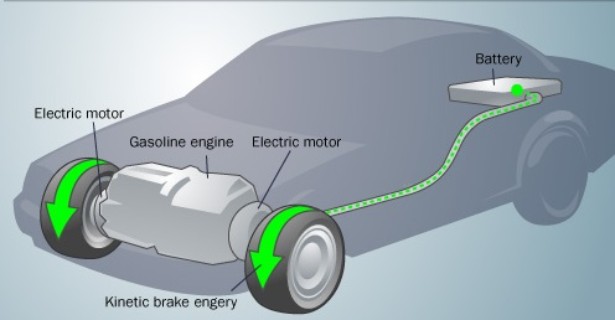
When starting an EV, the battery powers the motor, which spins the wheels. This is called “spinning off” the car. While the motor is spinning, the brakes are also being applied. The EV is being “regenerated” as the car is being pushed by the motor while the brakes are being used. Regenerative braking allows the car to be started without using the brakes in normal driving conditions. As the motor slows down, the battery charges and is ready to power the car again.
Advantages of EVs without transmissions
– Less weight – and therefore more fuel efficient – than a traditional car with a transmission. – Less maintenance than conventional cars with a transmission. – Easier to park and drive. There is no clutch and no transmission to slip or break. – Better for urban and public parking. – More eco-friendly and cost effective than a hybrid EV, which combines the advantages of an EV with those of a regular car with a clutch. – More comfortable on long road trips. – No need to change oil or get an oil change.
Disadvantages of EVs without transmissions

– No torque – axle-slip – and will not climb steep hills quickly. – Low initial acceleration and top speed. – No hill-start assist that can help restart the engine in the event of a breakdown. – Engine may need regular maintenance and tune-ups, as compared to internal combustion engines, which do not require maintenance. – Cannot drive on highways or on long trips, like the range available in EV hybrids. – Must charge their batteries overnight. – No assurance of long-term reliability and safety, as compared to internal combustion engines.
Final Words
Electric vehicles are making their mark in the transportation industry. With the growing concern about climate change and pollution, more and more people are switching to better and greener transportation, like an electric car. These vehicles are known for their quiet, smooth, and eco-friendly operation. They are also much cheaper to fuel than traditional cars. However, they do have some drawbacks, including their limited range and torque. These EVs work differently from a car that has a transmission. There is no clutch or transmission, which means that they have no torque and can only go very slowly. These are some of the things to keep in mind when purchasing an EV without a transmission.







